Sansui Medical
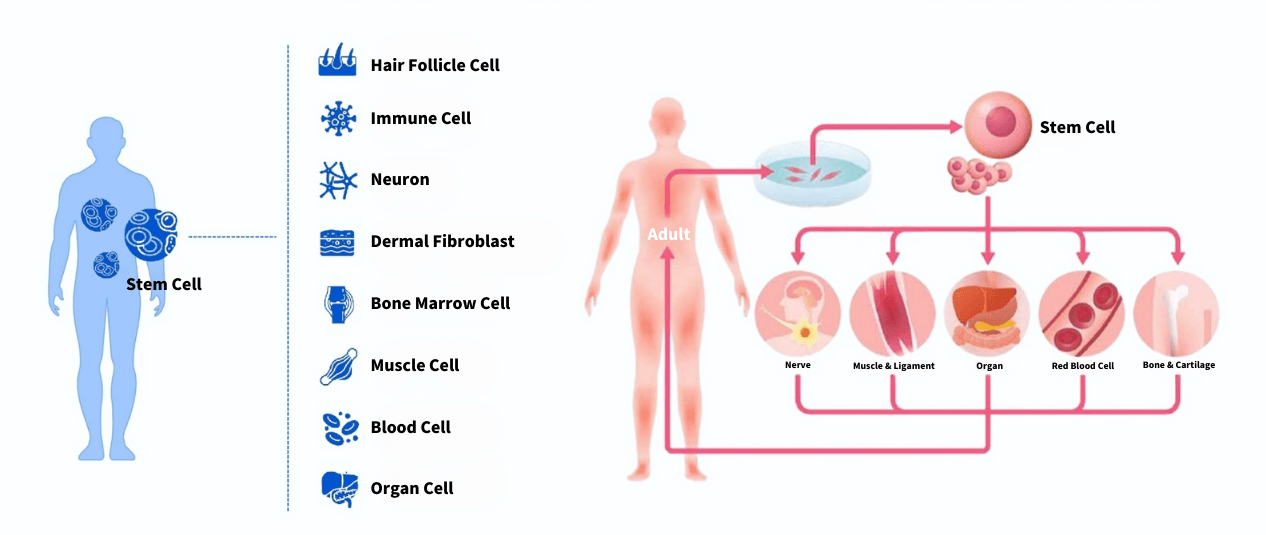
A therapeutic approach aimed at restoring functions damaged by disease or injury. Patient-derived stem cells are collected, expanded, and reinfused to promote regeneration of impaired tissues or organs.
It offers new options for previously hard-to-treat diseases and is at the forefront of modern medicine.
Stem cells can self-renew and differentiate into many cell types—bone, nerve, muscle, etc.—and are widely used in tissue repair, organ regeneration, and chronic disease treatment.
In Japan, autologous stem cells (from the patient) are commonly used to avoid immune rejection.
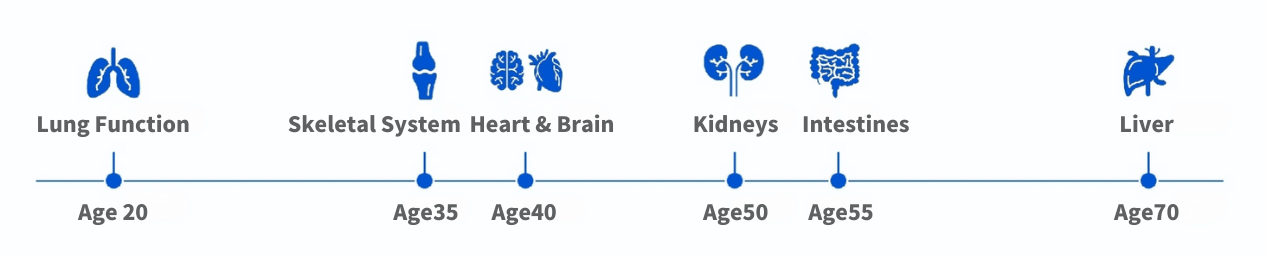
Are wrinkles and gray hair the only signs of aging? In fact, organ decline begins before outward changes appear. Studies suggest average healthy adults have ~80% organ function at age 40 and ~70% at 50; with age, decline accelerates, leaving only ~35% by age 70.
When stem cells decrease or lose function, the body’s ability to repair tissues and organs diminishes, leading to persistent diseases. If damage is repaired in time, disease may not occur or may resolve quickly.
Fundamental repair:restore damaged tissues for curative outcomes.
Fewer side effects:autologous cells avoid rejection.
Faster recovery:less burden than surgery with quicker rebound.

Cardiovascular:myocardial regeneration, heart failure, etc.
Metabolic:diabetes, hyperlipidemia, etc.


Neurological:cerebral infarction, Parkinson’s, spinal cord injury, etc.
Immune:immunodeficiency, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Orthopedic:knee osteoarthritis, bone defects, etc.
